
The network above should be configured and routed with OSPFv3. The network address is 2a03:f3a2:a2b2:xy00::H/64.
Set up a new config and set the link-local addess because it is needed for OSPFv3. Afterwards set the directly connected ip addresses.

OSPF Configration:
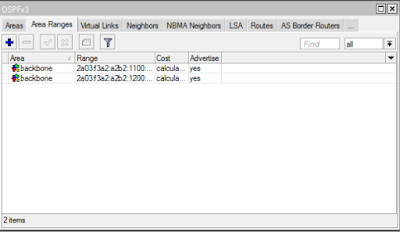
Configure a bridge to configure the Router-ID, the addresses and the interfaces. You are able to see the routes now.

System->Logging shows the transmitted data for OSPF.
You are able to see that IP-addresses are only transmitted if the network changes.











